GA: Genetic Algorithm#
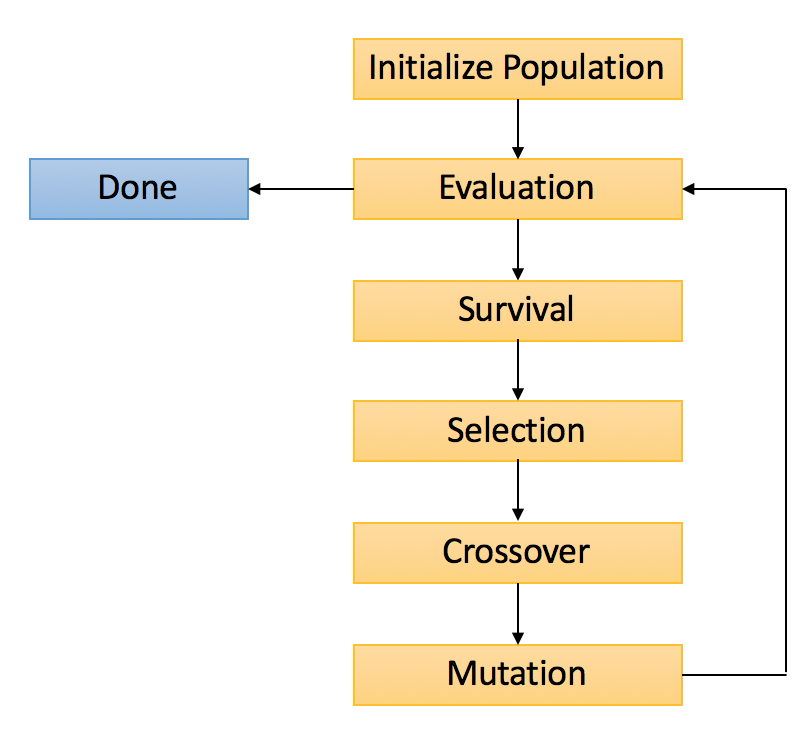
This class represents a basic (\(\mu+\lambda\)) genetic algorithm for single-objective problems. The figure below shows the flow of a genetic algorithm in general. In the following, it is explained how pymoo can be customized.
Initial Population: A starting population is sampled in the beginning. In this framework, this can be either a Sampling object, which defines different initial sampling strategies, or
Populationwhere theXandFvalues are set, or a simple NumPy array (pop_size x n_var).Evaluation: It is executed using the problem defined to be solved.
Survival: It is often the core of the genetic algorithm used. For a simple single-objective genetic algorithm, the individuals can be sorted by their fitness, and survival of the fittest can be applied.
Selection: At the beginning of the recombination process, individuals need to be selected to participate in mating. Depending on the crossover, a different number of parents need to be selected. Different kinds of selections can increase the convergence of the algorithm.
Crossover: When the parents are selected, the actual mating is done. A crossover operator combines parents into one or several offspring. Commonly, problem information, such as the variable bounds, are needed to perform the mating. For more customized problems, even more, information might be necessary (e.g. current generation, diversity measure of the population, …)
Mutation: It is performed after the offsprings are created through the crossover. Usually, the mutation is executed with a predefined probability. This operator helps to increase the diversity in the population.
Example#
[1]:
from pymoo.algorithms.soo.nonconvex.ga import GA
from pymoo.problems import get_problem
from pymoo.optimize import minimize
problem = get_problem("g1")
algorithm = GA(
pop_size=100,
eliminate_duplicates=True)
res = minimize(problem,
algorithm,
seed=1,
verbose=False)
print("Best solution found: \nX = %s\nF = %s" % (res.X, res.F))
Best solution found:
X = [1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.
1. 1. 1. 2.99221525 2.9943655 2.99054298
1. ]
F = [-14.97712372]
API#
- pymoo.algorithms.soo.nonconvex.ga.GA(pop_size=100, sampling=<pymoo.operators.sampling.rnd.FloatRandomSampling object>, selection=<pymoo.operators.selection.tournament.TournamentSelection object>, crossover=<pymoo.operators.crossover.sbx.SBX object>, mutation=<pymoo.operators.mutation.pm.PM object>, survival=<pymoo.algorithms.soo.nonconvex.ga.FitnessSurvival object>, eliminate_duplicates=True, n_offsprings=None, output=<pymoo.util.display.single.SingleObjectiveOutput object>, **kwargs)[source]